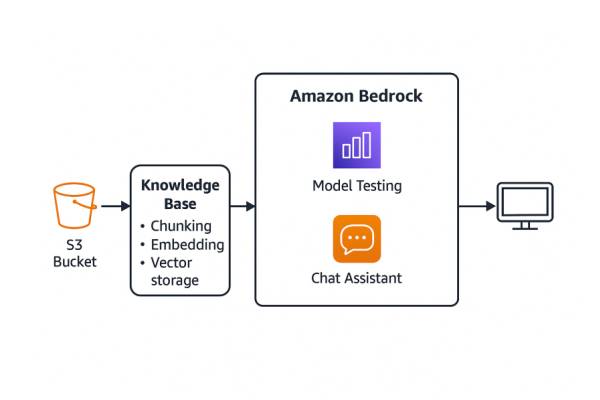
Anthropic is a leading company in artificial intelligence research and development, best known for its large language model, Claude. The Claude.ai and Claude Code product lines have become especially popular among software developers in recent years due to their strong code generation abilities and excellent performance in automation.
In a recent survey, Anthropic analyzed 500,000 coding interactions to better understand how developers use these models. The analysis divided the conversations into two categories: Claude.ai, which represents the standard chatbot interface, and Claude Code, which is designed specifically for coding tasks. Researchers looked at how often the AI worked in an "automated" way (completing tasks on its own) versus a "collaborative" way (working together with humans).
Three main trends were observed:
1. Growing Interest in Automation 79% of Claude Code conversations were focused on automation, compared to only 49% for Claude.ai. Both tools supported feedback loops and directive automation (where tasks are done with little human input), but these features appeared more often with the coding-focused agent. This suggests that as LLM-based agents become more common, software development is likely to become more automated.
2. More User-Friendly Applications The most frequently used programming languages were from the web development stack: JavaScript and TypeScript (31%), as well as HTML and CSS (28%). Common tasks included creating UI/UX components (12%) and building web or mobile applications (8%). This shows that “vibe coding” – where developers give natural language instructions to the AI – is especially useful when designing user interfaces.
3. Startups as Early Adopters Startup projects made up 33% of Claude Code usage, while enterprise applications only accounted for 13%. This reflects the difference between early and late adopters. Fast-moving, innovative companies are more likely to benefit from the productivity boost offered by new AI tools.
However, the analysis has some limitations. It only included interactions with Claude.ai and Claude Code — not with Claude Team, Enterprise, or API users — and some user contexts were estimated. Also, the study did not consider the regular cycles of software development, like sprint planning.
Looking ahead, a key question is how long feedback loops will remain the dominant method and when AI agents will be able to handle more complex tasks with little human help. As AI continues to advance, the role of developers may shift — from writing detailed code to managing, monitoring, and fine-tuning AI systems. Software development might become a model for how other professions will be transformed by the growing power of LLMs.